LCA算法之倍增法
Contents
问题
一个有$n$个节点的树,求任意两点$u,v$的最近公共祖先$lca$(Lowest common ancestor)
最近公共祖先定义
在一棵没有环的树上,每个节点肯定有其父亲节点和祖先节点,而最近公共祖先,就是两个节点在这棵树上深度最大的公共的祖先节点。 换句话说,就是两个点在这棵树上距离最近的公共祖先节点。
所以LCA主要是用来处理当两个点仅有唯一一条确定的最短路径时的路径。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lowest_common_ancestor https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/最近公共祖先_(图论)
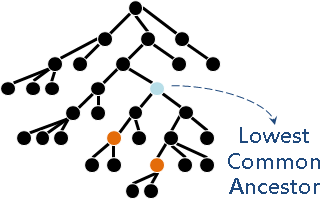
以下图:
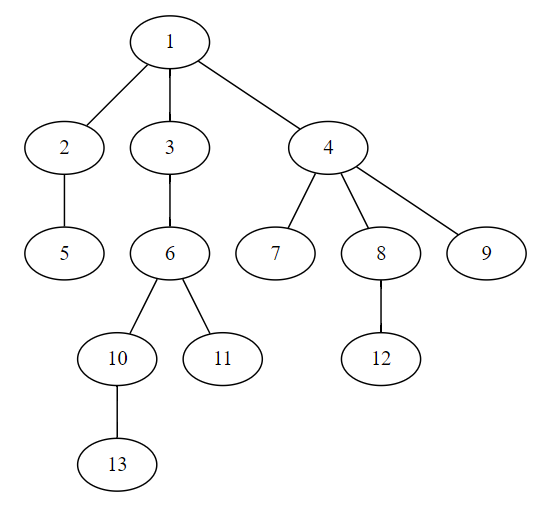
例如: $LCA(13,11)=6$ $LCA(10,11)=6$ $LCA(5,11)=1$ $LCA(7,4)=4$ (注意:节点也是自己的祖先)
朴素算法
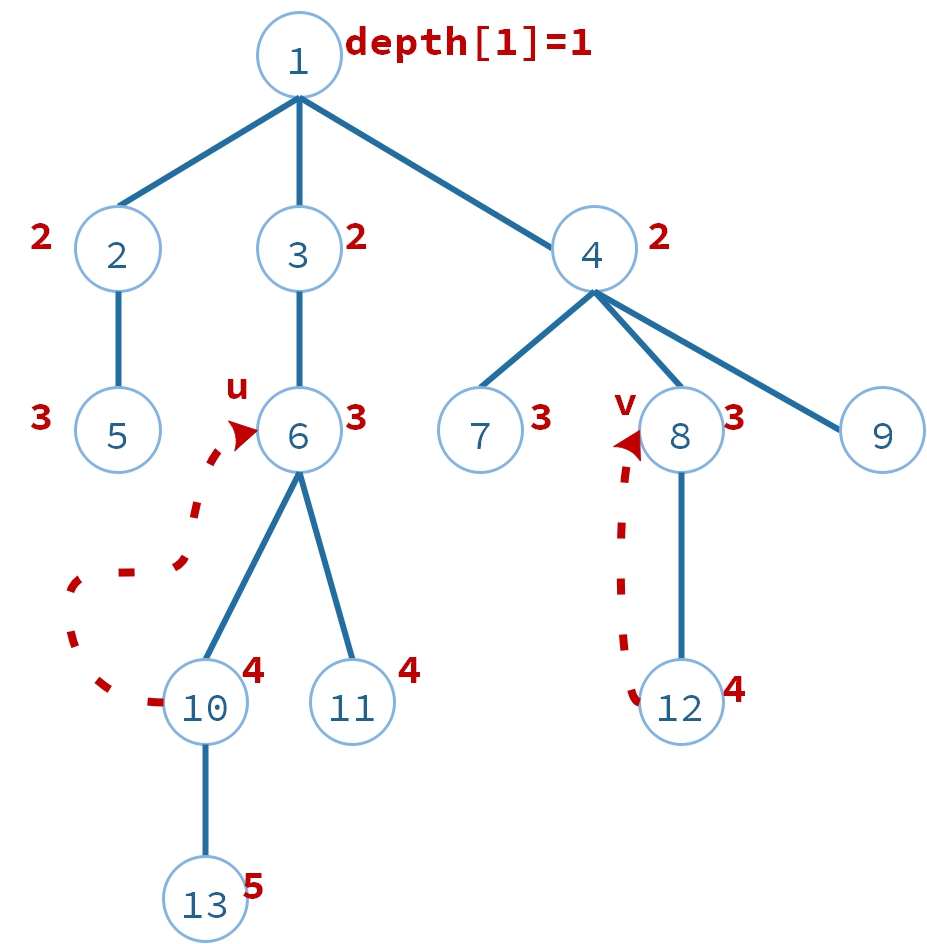
$u=13,v=12,LCA(u,v)=?$
求$LCA(13,12)=?$
- 计算节点深度: 从根节点深度搜索一次树,计算每一个节点的深度$depth[i]$,时间复杂度$O(n)$。
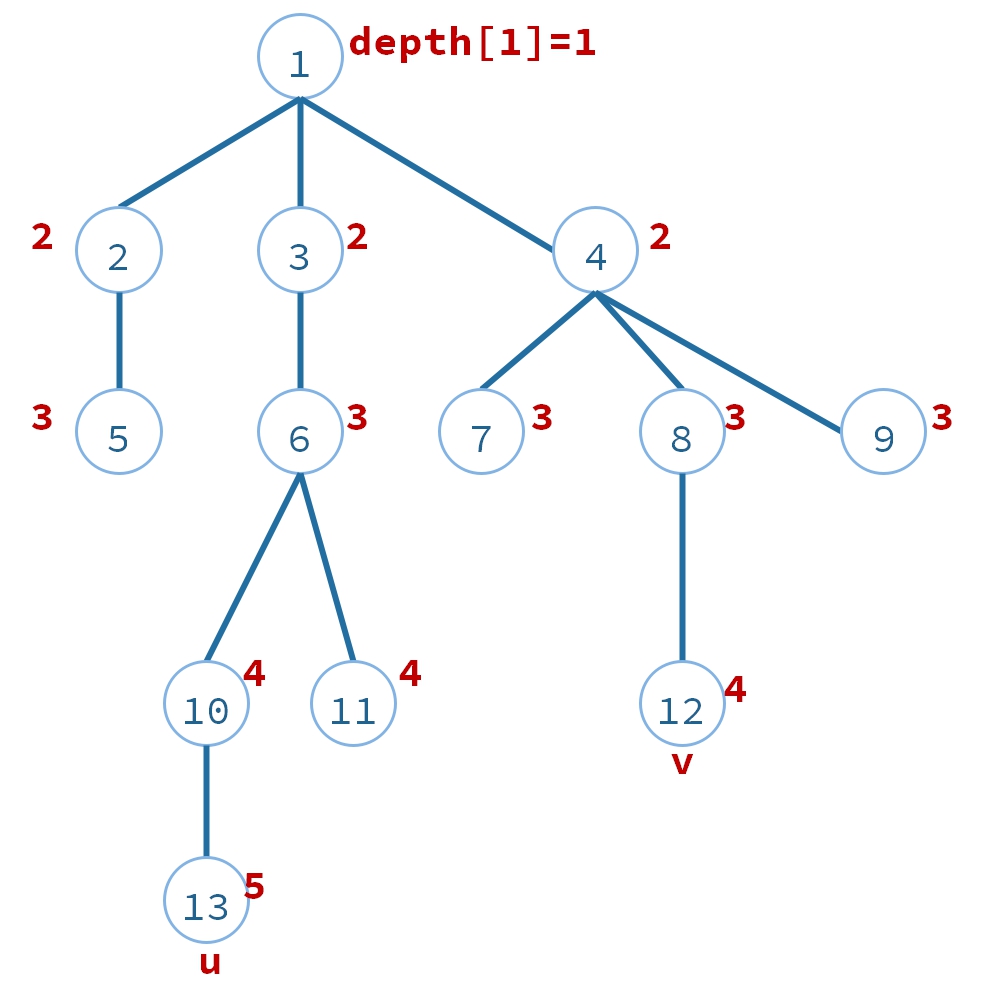
- 平衡两点深度: 如果$depth[u] \neq depth[v]$,把深度比较大深的往上移动,使得$depth[u] = depth[v]$。时间复杂度$O(\mid p-q \mid)$,期中p,q表示这两个节点的深度。
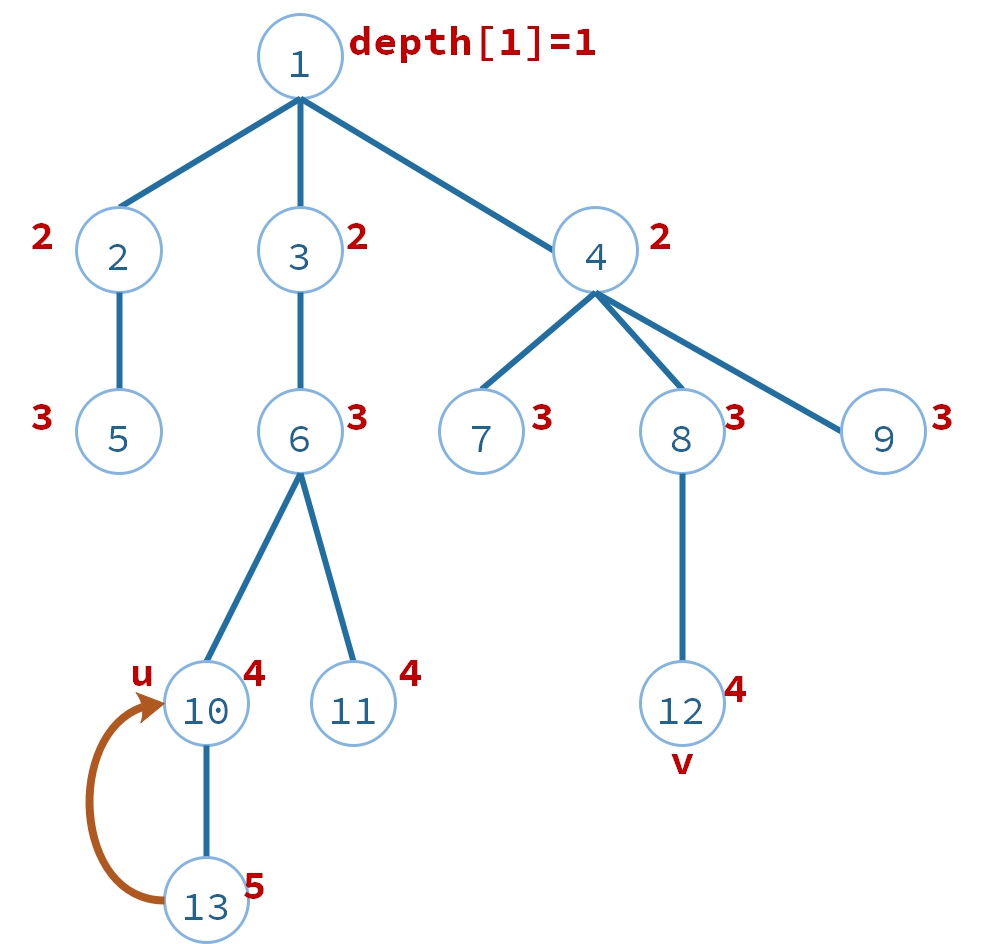
把$u=13$ 这个点往上移动(往父节),使得$u=10$。此时$depth[12] = 4,depth[12] = 4$。
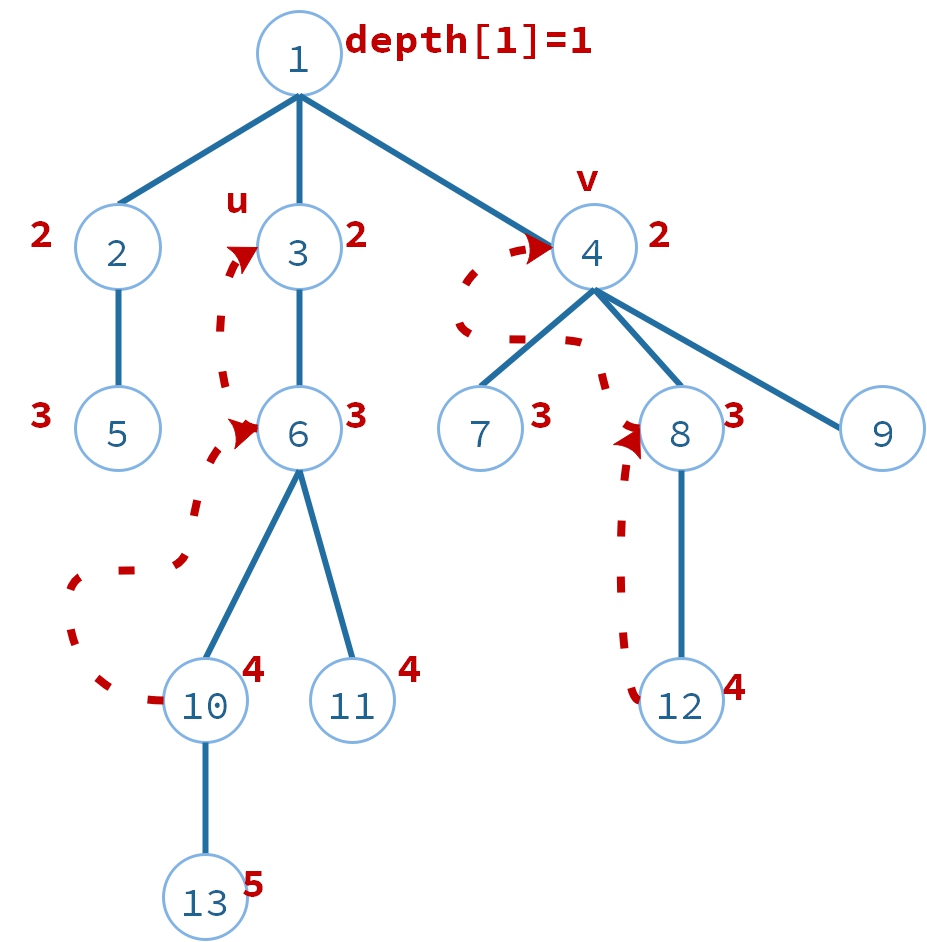
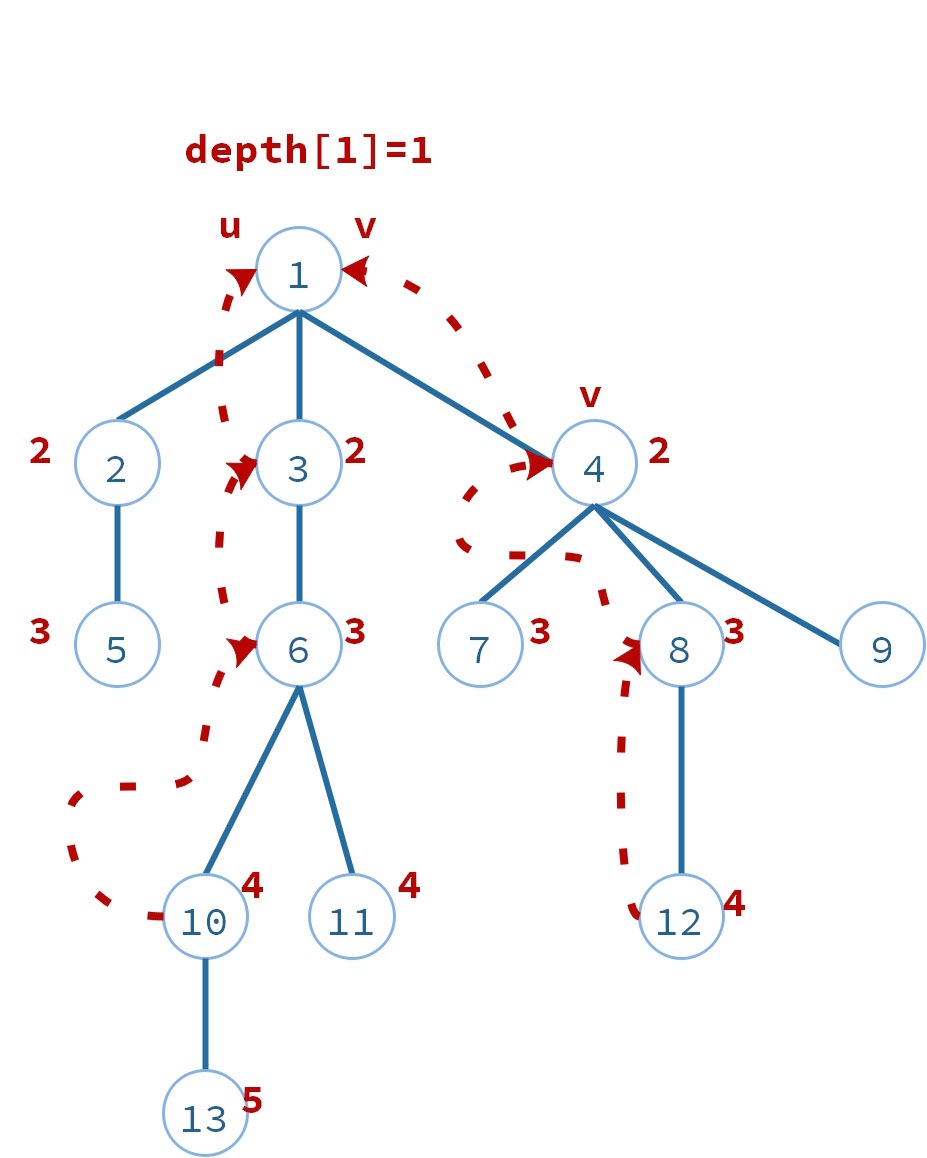
- 同时移动两点,直到相同: $u$,$v$每次同时往上移动一步,直到$u=v$,这时候就是LCA的答案,时间复杂度:$O(n)$ 如下图:
倍增算法
思路
以上第2、3步骤,每次都移动一步。时间复杂度$O(\mid p-q \mid) + O(n)$。
还可以快一点。一口气移动m步。
- 预先计算好每个节点的上一辈祖先,上两辈祖先,上四辈祖先,上八辈祖先,….,上$2^k$辈祖先,$k=\log_2(n)$;
- 二分查找LCA; 2.1 辈分太高,祖先相等或超出根节点,缩减一半。 2.2 辈分太低,祖先是两个不同节点,未到达共同祖先,移动节点。 2.2 直到找到第一个祖先不重叠的的节点
说明
- 寻找u,v的LCA
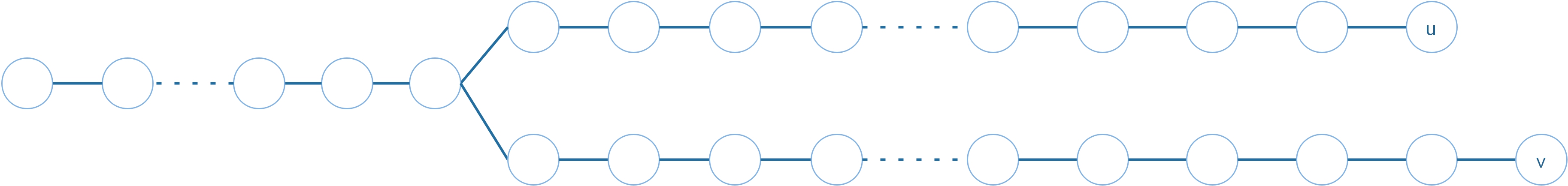
- 移动v,使得u、v深度相同
- 开始跳跃
3.1 跳跃最大处:$2^{k+1}$
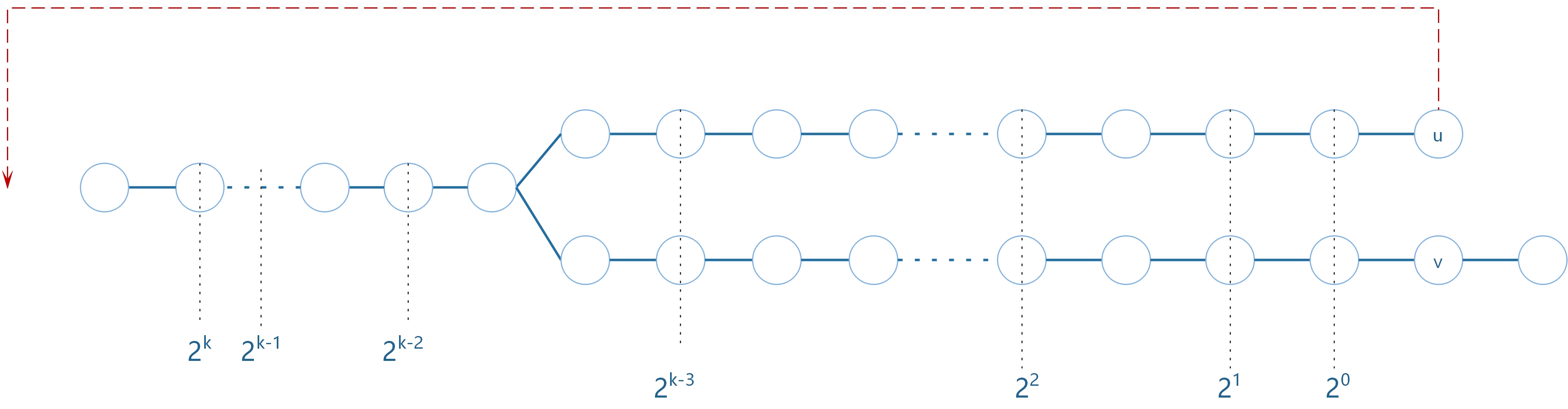 3.2 发现祖先相同,太多,缩减一半。$2^{k}$
3.2 发现祖先相同,太多,缩减一半。$2^{k}$
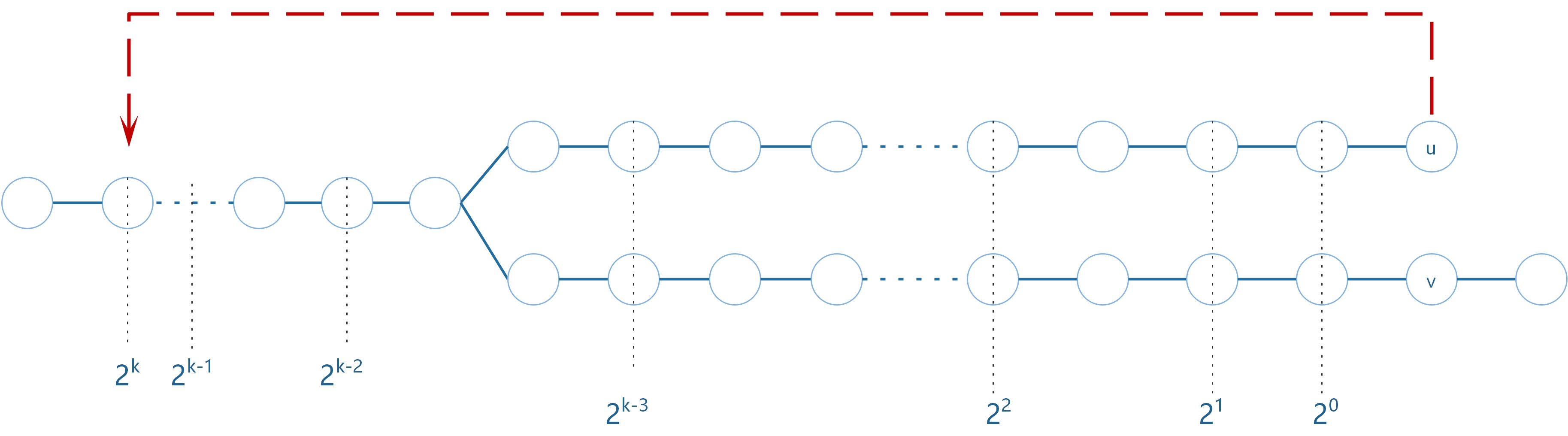 3.3 祖先相同,还是太多,重复缩减一半。$2^{k-1}…$
3.3 祖先相同,还是太多,重复缩减一半。$2^{k-1}…$
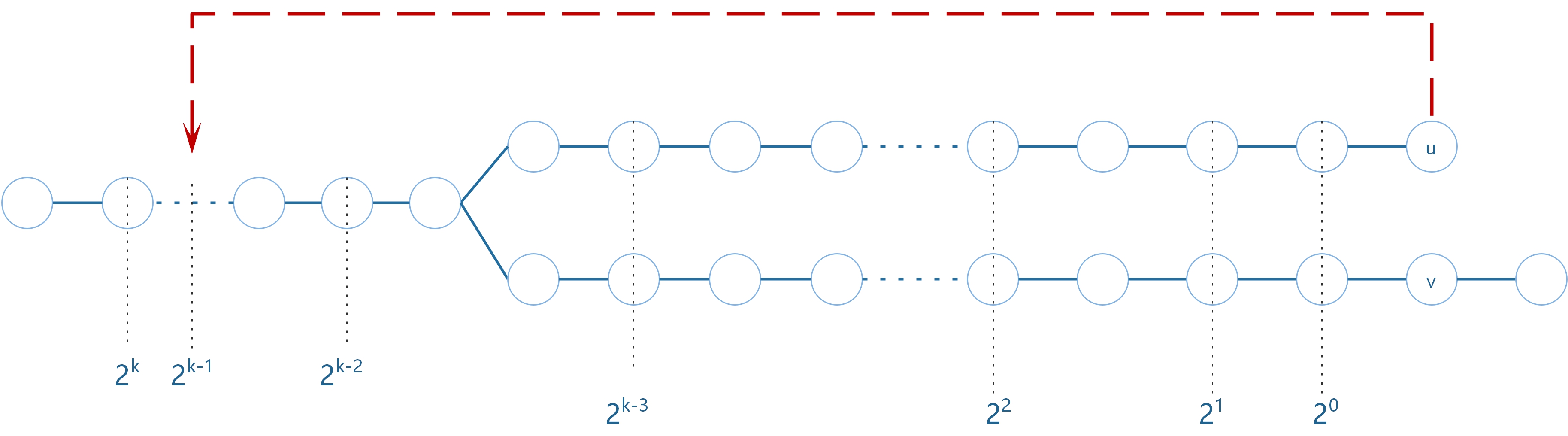
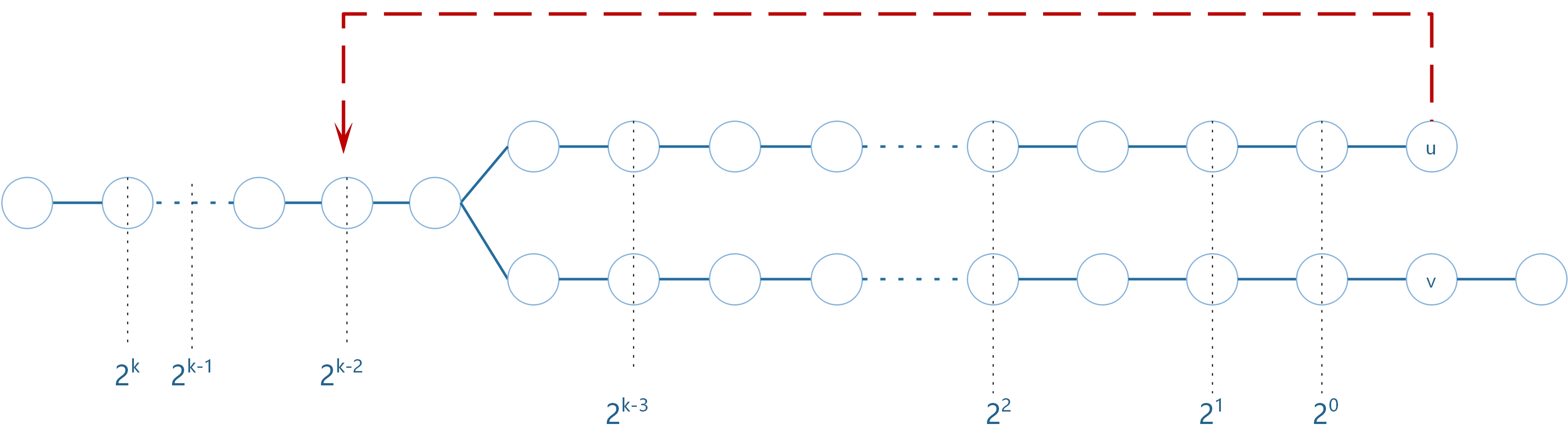 3.4 发现祖先不同,停止缩减。$2^{k-3}$
3.4 发现祖先不同,停止缩减。$2^{k-3}$
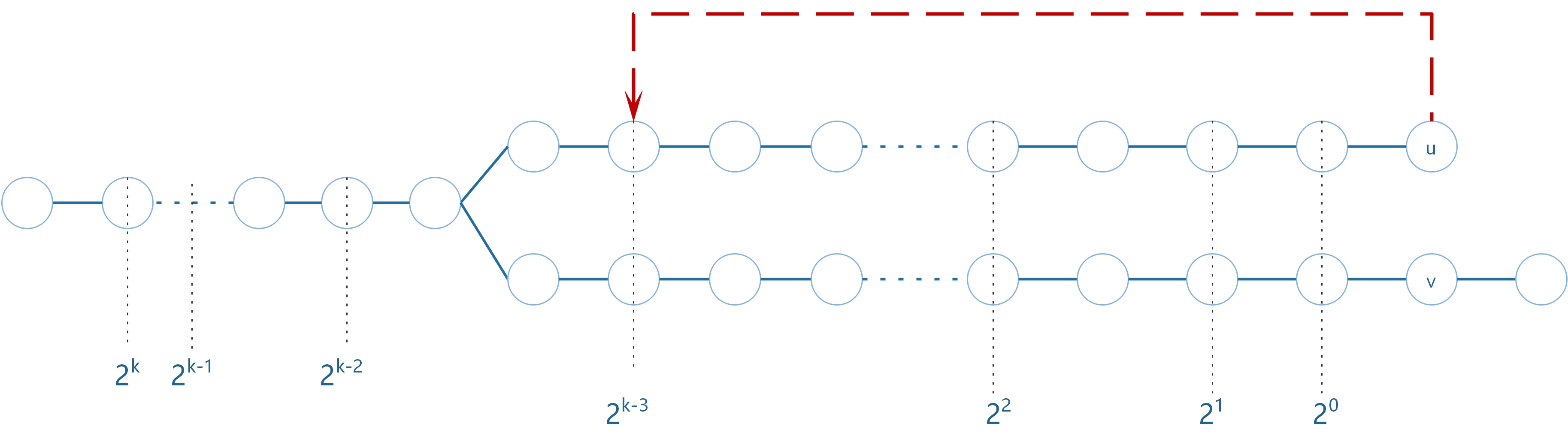 3.5 移动u,v到这个位置,重复跳跃。前面已经跳了$3$次。此刻从$2^{k-3}$开始跳跃
3.5 移动u,v到这个位置,重复跳跃。前面已经跳了$3$次。此刻从$2^{k-3}$开始跳跃
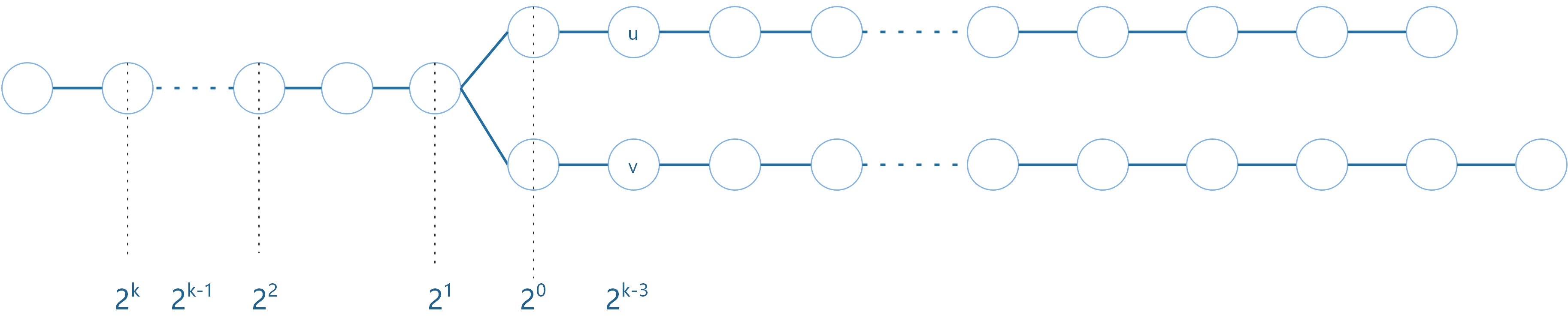 3.6不断重复跳跃,可以跳到离u,v最远,且不同的祖先
3.6不断重复跳跃,可以跳到离u,v最远,且不同的祖先
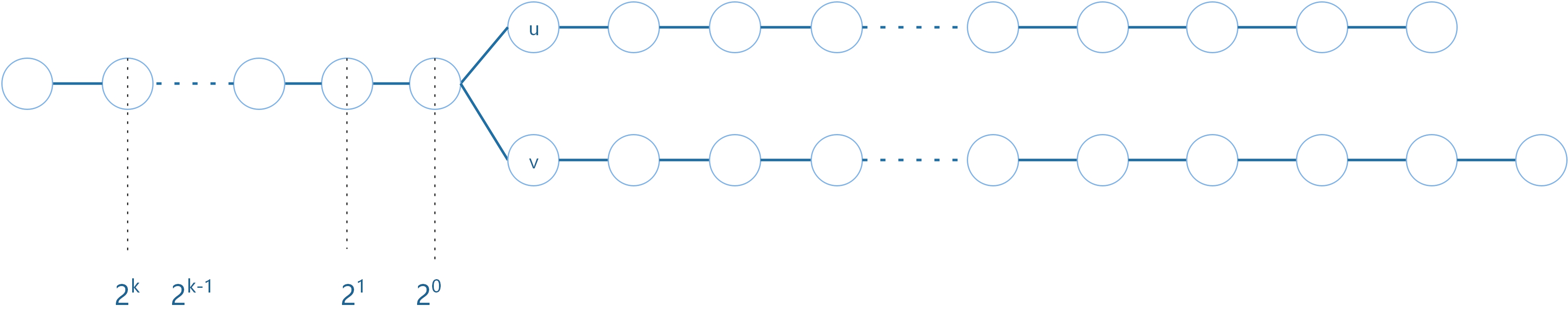 3.7上一步(3.6)的父亲就是LCA
3.7上一步(3.6)的父亲就是LCA
原理
理论上 u 的所有祖先都可以根据ancestors数组多次跳转得到,因为理论上任意证整数都可以由$2^n$累加构成,例如:
$log_2(69)=6.10852$
$ 69 二进制: 01000101 = 2^6+2^2+2^0$
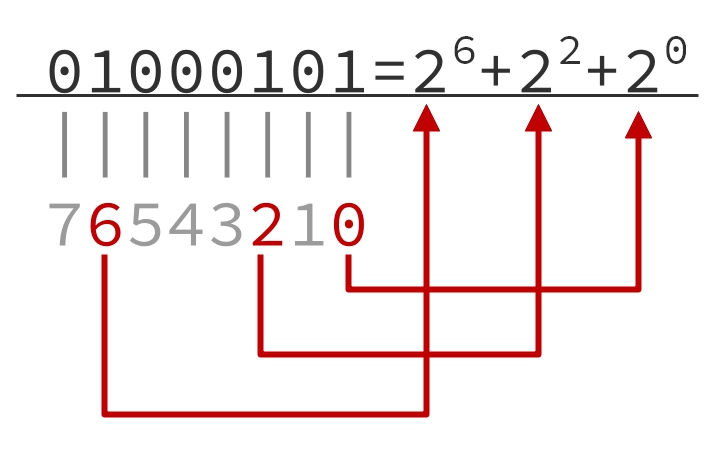
贪心法:
- $ \color{Red}{2^7} > 69$
- $ {2^6} < 69$
- $ 2^6+\color{Red}{2^5} > 69$
- $ 2^6+\color{Red}{2^4} > 69$
- $ 2^6+\color{Red}{2^3} > 69$
- $ 2^6+\color{Red}{2^2} < 69$
- $ 2^6+2^2 + \color{Red}{2^1} > 69$
- $ \color{blue}{2^6+2^2 + 2^0 = 69}$
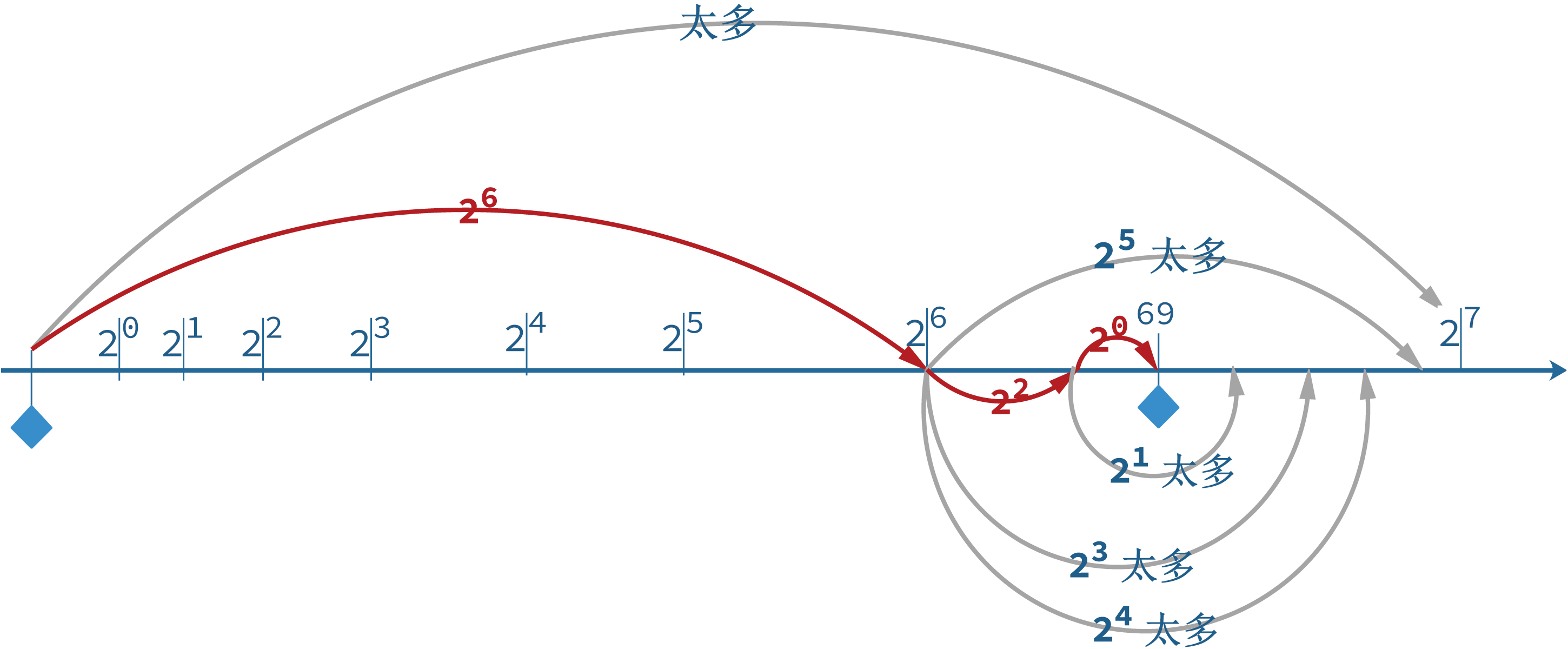
$ 01001111 (79)=2^6+2^3+2^2+2^1+2^0$
代码
- 变量声明和初始化
|
|
- 记录各节点i的深度depth[i]。dfs一遍即可O(N)。
|
|
- 预处理倍增数组,$ancestors[i][j]$表示节点$i$往上(往根的方向)跳$2^j$步的祖先节点编号。0表示不存在节点,也就是跳过根了。$ancestors[i][0]$是节点$i$的父节点标号。 递推关系:$ancestors[i][j] = ancestors[ancestors[i][j-1]][j-1]$
因为:$2^j=2^{j-1}+2^{j-1}$
所以: $ancestors[i][0] = parent[v]$ $ancestors[i][1] = ancestors[ancestors[i][0]][0]$ $ancestors[i][2] = ancestors[ancestors[i][1]][1]$ $ancestors[i][3] = ancestors[ancestors[i][2]][2]$ $ancestors[i][j] = ancestors[ancestors[i][j-1]][j-1]$
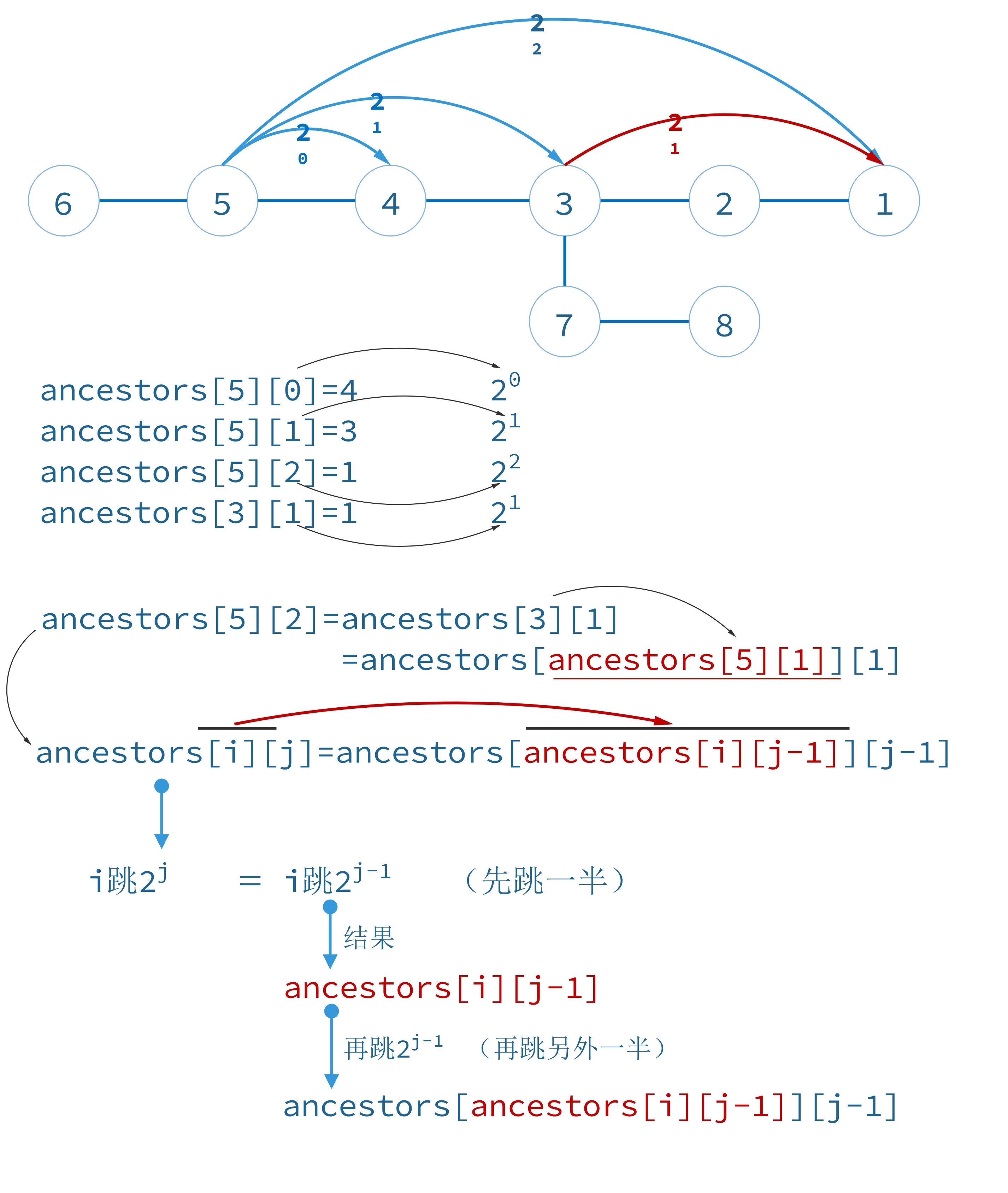
原理:$2^j=2^{j-1}+2^{j-1}$
|
|
- 查找u,v的LCA
|
|
5.快速计算$log_2(n)$,位运算:$(1«i) = 2^i$
|
|
总结
- 倍增算法(英文名:Binary Lifting)是在线算法,适合查询数量比较少的情况。时间复杂度在$O(log(n))$ ~ $O(n*log(n))$之间。
- 还有一种离线算法Tarjan,适合查询数量比较多的情况。
参考
https://zhyack.github.io/posts/2015_12_22_LCA-Binary-Lifting-Note.html
http://www.csie.ntnu.edu.tw/~u91029/Tree.html#5
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/lca-in-a-tree-using-binary-lifting-technique/
https://cp-algorithms.com/graph/lca_binary_lifting.html
https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/22325
https://iq.opengenus.org/binary-lifting-k-th-ancestor-lowest-common-ancestor/
https://acmcairoscience.wordpress.com/2015/04/07/lowest-common-ancestor-finding-of-o-log-n-binary-lifting-method/
http://rahul-walkar.blogspot.com/2017/07/lca-binary-lifting-and-hld.html
题目
Nearest Common Ancestors
http://poj.org/problem?id=1330
LCA - Lowest Common Ancestor
https://www.spoj.com/problems/LCA/
DISQUERY - Distance Query
https://www.spoj.com/problems/DISQUERY/
Tourists
https://open.kattis.com/problems/tourists
A and B and Lecture Rooms
https://codeforces.com/contest/519/problem/E
Lynyrd Skynyrd (倍增思想)
https://codeforces.com/contest/1143/problem/E
题目清单
https://a2oj.com/category?ID=208
https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/43917
https://cp-algorithms.com/graph/lca.html
Author Shawn
LastMod 2019-12-22